



ECMAScript (JavaScript)



on the client

on the server
ES5 / classic JavaScript...
...has nothing in common with Java * except for some key words
...is more like Lisp in C's clothing
*Douglas Crockford
...has objects, but is class-free
...is of single-threaded nature
...has asynchronous programming model
...is object oriented & functional at the same time
Checkout backup slides for javascript history
Classic JavaScript has very confusing concepts (at least for Java / .Net devs...). Here are a few...
this is function scoped instead of block scoped===)JavaScript that scales.
TypeScript is a typed superset of JavaScript that compiles to plain JavaScript.
Any browser. Any host. Any OS. Open source.
Let's start with the quickstart example from typescriptlang.org
function greeter(person) {
return "Hello, " + person;
}
let user = "Jane User";
document.body.innerHTML = greeter(user);
Could be written in TypeScript...
function greeter(person: string) {
return "Hello, " + person;
}
let user = "Jane User";
document.body.innerHTML = greeter(user);
...and be type safe...
function greeter(person: string) {
return "Hello, " + person;
}
let user = [0, 1, 2];
document.body.innerHTML = greeter(user);
Leads to compile time error.
error TS2345: Argument of type 'number[]' is not assignable to parameter of type 'string'.
... and is even supported by VS Code

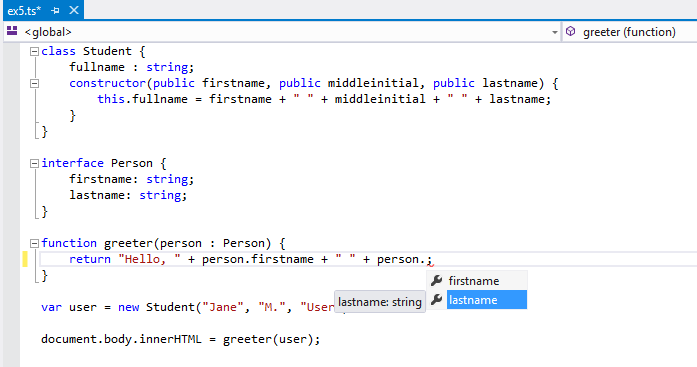
TypeScript works well with VS Code
interface Person {
firstName: string;
lastName: string;
}
function greeter(person: Person) {
return "Hello, " + person.firstName + " " + person.lastName;
}
let user = { firstName: "Jane", lastName: "User" };
document.body.innerHTML = greeter(user);
In TypeScript, two types are compatible if their internal structure is compatible.
interface OnInit {
ngOnInit(): void
}
class MyComponent implements OnInit {
ngOnInit(): void {
console.log('Component activated.')
}
}
Interfaces can be implemented.
abstract class Speaker {
constructor(protected location: string) { }
abstract speak(): void;
}
class Headphones extends Speaker {
constructor() {
super('in ear');
}
speak(): void {
console.log(this.location + ': la la la');
}
}
function play(speaker: Speaker) {
speaker.speak();
}
play(new Headphones()); // in ear: la la la
Classes
class A {
name: string;
}... compile to
var A = (function () {
function A() {
}
return A;
}());Interfaces
interface A {
name: string;
}... compile to nothing.
Interfaces define contracts.
function sayHelloTo(person: { name: string }) {
console.log(person.name);
}... using Interfaces
interface NamedPerson {
name: string;
}
function sayHelloTo(person: NamedPerson) {
console.log(person.name);
}
let x = [1, 2, 3]; // x becomes number[]
// zoo becomes (Rhino | Elephant | Snake)[]
let zoo = [new Rhino(), new Elephant(), new Snake()];
// corrects type
let zoo: Animal[] = [new Rhino(), new Elephant(), new Snake()];
function padLeft(value: string, padding: any) {
if (typeof padding === 'number') {
return Array(padding + 1).join(' ') + value;
}
if (typeof padding === 'string') {
return padding + value;
}
throw new Error(`Expected string or number, got '${padding}'.`);
}
interface MyType {
name: string;
}
function myFunc(val: MyType) {
// ...
}
myFunc(null); // compiler error
myFunc(undefined); // compiler error
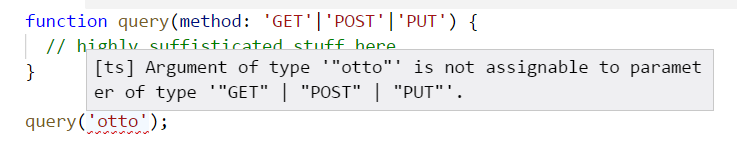
function query(method: 'GET'|'POST'|'PUT') {
// highly sophisticated stuff here...
}
query('otto');
will it compile?
More specific than a string - cool, right?
Live Code Examples & Backup slides below
Following slides are not subject of the lecture.
Ask trainers in case of questions.
ECMAScript (ES) first introduced 1997 turned 25 in 2022 and its popularity is still growing.
3th PYPL (September 2021), 7th TIOBE Index (September 2021)
(TypeScript is listed separately)
Can I use ES6 (Browsers Support)
node.green (Node.js Support)
An example for a well known JavaScript pattern (IIFE)
var person = (function () {
var details = {
firstName: 'John',
lastName: 'Example',
age: 30
};
return {
letMeIntroduceMyself: function () {
return 'My name is ' +
details.firstName + ' ' + details.lastName;
}
};
})();
person.letMeIntroduceMyself(); // My name is John Example
person.details; // undefined
Newer ES versions introduced concepts like classes, modules and block scope variables.
With TypeScript we can use those features today - and that's where we will continue.